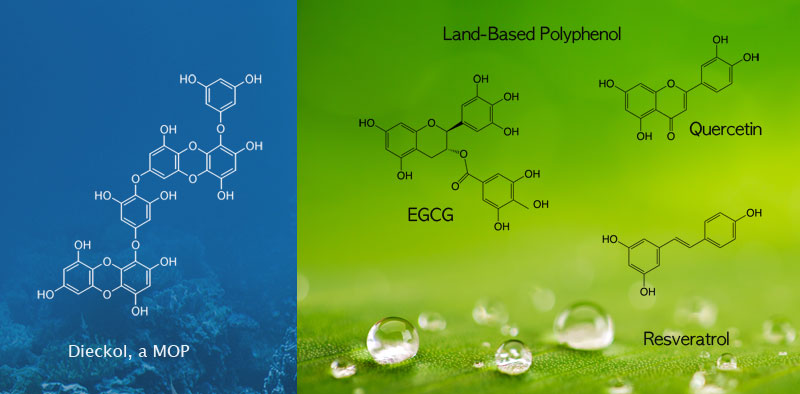
Molecular Structure of MOP
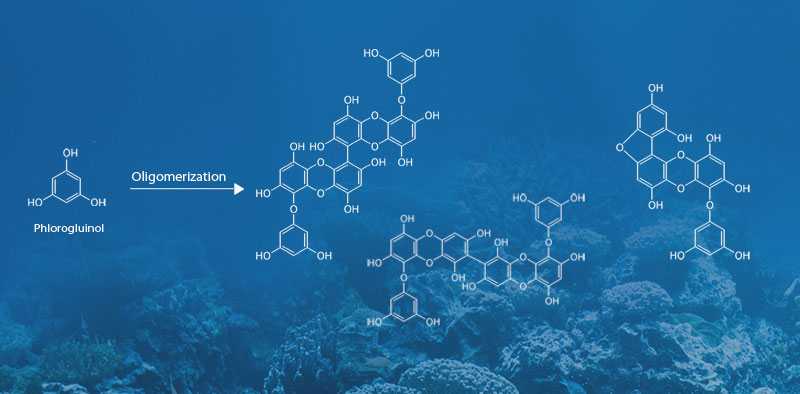
The uniqueness of MOP is that it is composed of diverse molecules that share the same chemical feature. The component molecules of MOP are made of only one monomer called "Phloroglucinol". In other words, the molecules of MOP are oligomers of phloroglucinol which works as a building block.
When we scrutinize the molecular structures of MOP a little bit, we can immediately notice that they have inside hydrophobic benzene rings together with outside multiple hydrophilic "hands" that can catalyze the formation of hydro-network with nearby water and biomolecules.